Electrical wire connectors are essential components in electrical systems, providing safe and reliable connections between wires. Choosing the right connector ensures the safety, efficiency, and longevity of electrical installations. This guide covers the main types of connectors, their uses, and tips for selecting the appropriate one for your needs.
Types of Electrical Wire Connectors
- Twist-On Wire Connectors
- Description: Also known as wire nuts or wire caps, these connectors have a conical shape with a threaded interior.
- Uses: Commonly used in residential and light commercial applications for joining multiple wires.
- Advantages: Easy to install, reusable, and provides a secure connection.
- Crimp Connectors
- Description: These connectors involve placing the wire into a metal barrel and using a crimping tool to compress the barrel around the wire.
- Uses: Widely used in automotive, industrial, and marine applications.
- Advantages: Offers a strong, vibration-resistant connection.
- Push-In Wire Connectors
- Description: These connectors allow wires to be inserted into holes that automatically grip the wire.
- Uses: Suitable for residential wiring projects.
- Advantages: Quick and easy to use, providing a reliable connection without the need for twisting or crimping.
- Screw Terminal Connectors
- Description: Consists of a screw that secures the wire in place by clamping it.
- Uses: Found in electrical panels, switches, and outlets.
- Advantages: Provides a strong, secure connection and allows for easy disconnection.
- Solder Connectors
- Description: Involves using solder to join wires, providing a solid and permanent connection.
- Uses: Common in electronics and applications requiring high reliability.
- Advantages: Creates a strong, permanent connection with excellent conductivity.
- IDC (Insulation Displacement Connectors)
- Description: These connectors cut through the insulation to make contact with the wire.
- Uses: Often used in telecommunications and networking.
- Advantages: Quick to install, without needing to strip the wire insulation.
Uses of Electrical Wire Connectors
- Residential Wiring: Connecting wires in electrical boxes, outlets, switches, and fixtures.
- Automotive Wiring: Connecting wires in vehicles, ensuring reliable connections in a vibration-prone environment.
- Industrial Applications: Connecting heavy-duty wires in machinery and equipment.
- Electronics: Joining small-gauge wires in circuit boards and electronic devices.
- Telecommunications: Connecting wires in phone systems and networking installations.
How to Choose the Right Connector
- Determine the Wire Gauge:
- Ensure the connector is compatible with the wire gauge. Using a connector designed for a different gauge can result in a poor connection.
- Consider the Environment:
- For outdoor or harsh environments, choose connectors that provide protection against moisture, dust, and temperature extremes.
- Check the Electrical Load:
- Ensure the connector can handle the current and voltage requirements of the application to prevent overheating and potential failure.
- Ease of Use:
- For quick and simple installations, push-in or twist-on connectors are convenient options. For more secure, permanent connections, crimp or solder connectors are preferred.
- Compliance with Standards:
- Ensure the connectors meet relevant electrical standards and certifications for safety and reliability.
- Reusability:
- If the connection may need to be disconnected and reconnected, choose connectors that allow for easy disassembly, like screw terminals or twist-on connectors.
Installation Tips for Electrical Wire Connectors
Proper installation of electrical wire connectors is vital for ensuring a secure and safe connection. Here are some tips to help you install various types of connectors effectively:
Twist-On Wire Connectors
- Strip the Wires:
- Strip the wire ends to the length specified by the connector manufacturer, usually around 1/2 to 3/4 inches.
- Align and Twist:
- Align the stripped ends of the wires together and twist them in the same direction as the threads of the connector.
- Install the Connector:
- Screw the connector onto the twisted wires until it is tight and secure. Ensure no bare wire is exposed.
Crimp Connectors
- Strip the Wires:
- Strip the wire ends to the appropriate length, typically about 1/4 inch.
- Insert the Wire:
- Insert the stripped wire into the metal barrel of the crimp connector.
- Crimp the Connector:
- Use a crimping tool to compress the barrel around the wire. Ensure a firm, tight crimp to avoid loose connections.
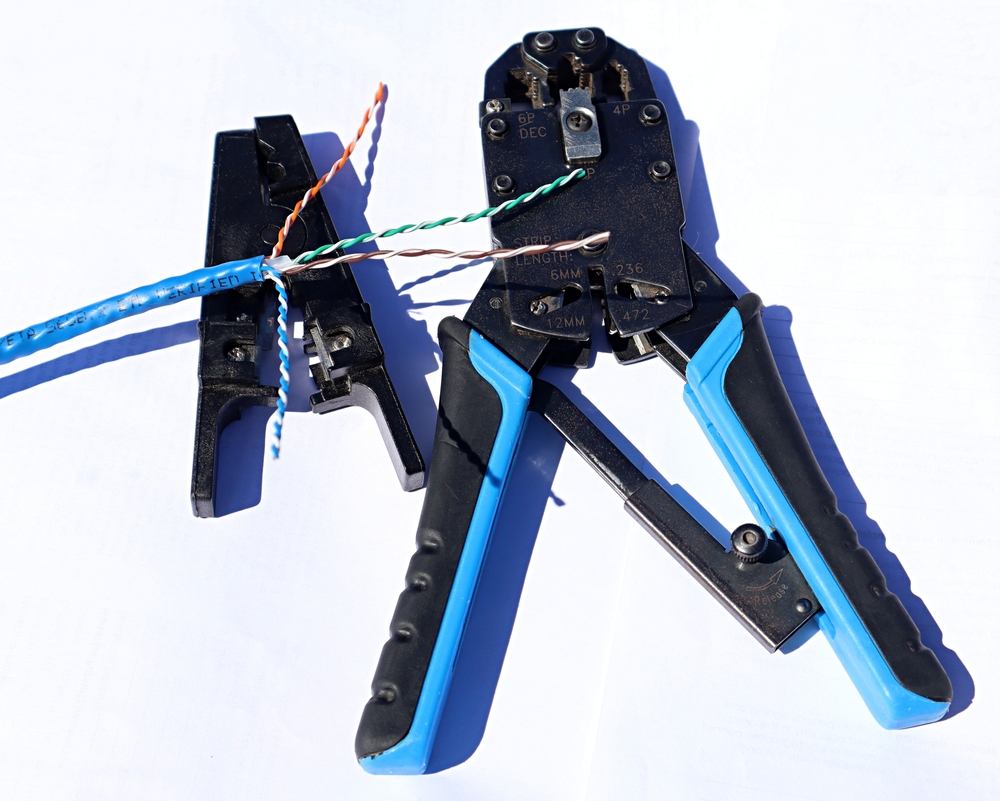
Push-In Wire Connectors
- Strip the Wires:
- Strip the wire ends to the specified length, usually around 1/2 inch.
- Insert the Wire:
- Push the stripped wire end into the hole of the connector until it clicks into place.
- Verify the Connection:
- Tug lightly on each wire to ensure it is securely held in the connector.
Screw Terminal Connectors
- Strip the Wires:
- Strip the wire ends to the required length, generally about 1/4 inch.
- Loosen the Screw:
- Loosen the screw on the terminal enough to insert the stripped wire end.
- Insert and Tighten:
- Insert the wire end under the screw and tighten the screw securely to clamp the wire in place.
Solder Connectors
- Prepare the Wires:
- Strip the wire ends to the necessary length, usually about 1/4 inch.
- Tin the Wires:
- Apply a small amount of solder to the stripped wire ends (tinning) to improve the solder connection.
- Solder the Connection:
- Heat the wires and apply solder until it flows and covers the joint. Allow the solder to cool and solidify.
Safety Considerations
When working with electrical wire connectors, safety should always be a priority. Here are some key safety considerations:
- Power Off:
- Always turn off the power to the circuit before working on any electrical connections to prevent shock or injury.
- Proper Tools:
- Use the correct tools for stripping, crimping, and connecting wires. This ensures a secure and reliable connection.
- Check Connections:
- Double-check all connections to ensure they are secure and there are no exposed wires that could cause a short circuit.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions:
- Always follow the connector manufacturer’s instructions for stripping length, wire insertion, and securing methods.
- Use Insulated Connectors:
- In situations where connections may be exposed to moisture or other environmental factors, use insulated connectors to protect against shorts and corrosion.
- Inspect Work:
- After completing the connections, inspect your work to ensure all connections are tight, properly insulated, and there are no loose wires.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter problems with electrical connections, here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
- Loose Connections:
- Check that all connectors are properly tightened and wires are securely held in place.
- Overheating:
- Ensure connectors are rated for the current and voltage of the circuit. Overheating may indicate an undersized connector or poor connection.
- Corrosion:
- Inspect connectors for signs of corrosion, particularly in outdoor or damp environments. Replace any corroded connectors.
- Intermittent Connections:
- Ensure that all wires are fully inserted into connectors and that there is no damage to the wire or connector.