Setting up home wiring for solar power involves several essential tips and considerations to ensure a safe and efficient system. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
1. Assessing Your Energy Needs
- Energy Audit: Conduct an energy audit to determine your household’s energy consumption. This helps in sizing your solar power system appropriately.
- Peak Usage: Identify your peak energy usage times to ensure your system can handle the load.
2. Solar Panel Placement
- Roof Inspection: Ensure your roof is in good condition and can support the weight of solar panels.
- Sunlight Exposure: Place panels where they will receive maximum sunlight, typically on south-facing roofs in the Northern Hemisphere.
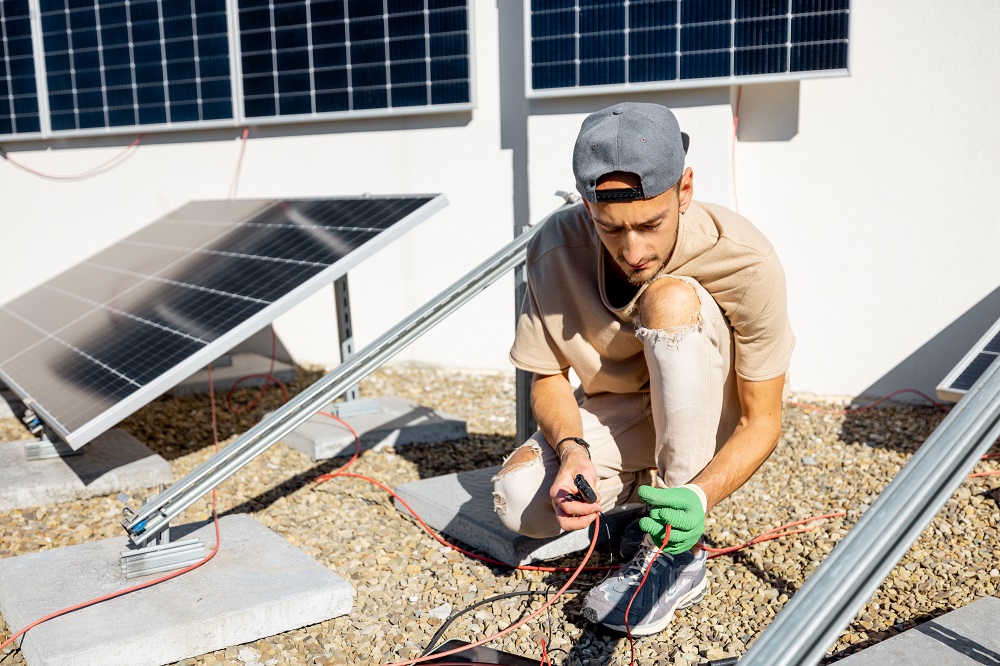

3. System Design
- Types of Systems: Decide between grid-tied, off-grid, or hybrid systems based on your needs and budget.
- Battery Storage: For off-grid and hybrid systems, consider the capacity and type of battery storage.
4. Electrical Components
- Inverters: Choose between string inverters, microinverters, or power optimizers. Inverters convert DC from panels to AC for home use.
- Charge Controllers: Essential for off-grid systems to prevent batteries from overcharging.
- Wiring and Connectors: Use appropriate gauge wires and connectors designed for solar systems to ensure safety and efficiency.
5. Safety Considerations
- Permits and Codes: Obtain necessary permits and adhere to local building codes and standards (e.g., NEC in the US).
- Grounding: Properly ground the system to prevent electrical shocks and ensure system safety.
- Surge Protection: Install surge protectors to protect the system from voltage spikes.

6. Installation Process
- Professional Installation: Consider hiring a certified solar installer to ensure compliance with regulations and safety standards.
- DIY Considerations: If opting for DIY, ensure thorough research and follow all guidelines strictly.
7. Maintenance and Monitoring
- Regular Inspections: Periodically check panels, wiring, and inverters for any issues.
- Cleaning: Keep panels clean from debris and dirt to maintain efficiency.
- Monitoring Systems: Use monitoring systems to track energy production and system performance.
8. Financial and Incentive Considerations
- Incentives and Rebates: Research available government incentives, rebates, and tax credits for installing solar power.
- Return on Investment: Calculate the ROI based on your initial investment, energy savings, and incentives.
9. Environmental Impact
- Sustainability: Consider the environmental benefits of reducing your carbon footprint.
- Recycling: Plan for the end-of-life disposal of panels and batteries responsibly.
10. System Scalability
- Future Expansion: Plan your system with future scalability in mind. Ensure your inverter and other components can handle additional panels if you decide to expand.
- Modular Components: Use modular components that can easily integrate with your existing system to facilitate upgrades.
11. Backup Power
- Generators: For off-grid or hybrid systems, consider having a backup generator to ensure a continuous power supply during prolonged cloudy periods or system maintenance.
- UPS Systems: Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems can provide short-term backup power and protect sensitive electronics.
12. Energy Efficiency
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: Invest in energy-efficient appliances and lighting to reduce your overall energy consumption, thereby maximizing the benefits of your solar power system.
- Insulation and Weatherproofing: Improve home insulation and weatherproofing to reduce heating and cooling energy requirements.
13. System Integration
- Smart Home Integration: Integrate your solar power system with smart home technology to optimize energy use and enhance convenience.
- Energy Management Systems: Use energy management systems to monitor and control energy usage, ensuring efficient use of generated power.
14. Warranty and Support
- Component Warranties: Ensure that all components, including panels, inverters, and batteries, come with comprehensive warranties.
- Installer Support: Choose installers who offer ongoing support and maintenance services.
15. Environmental and Aesthetic Considerations
- Roof Aesthetics: Consider the visual impact of solar panels on your roof. Some systems offer low-profile or integrated designs that blend with roofing materials.
- Landscaping: If using ground-mounted systems, ensure that they do not interfere with landscaping or other property uses.
16. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
- Zoning Laws: Verify that your solar installation complies with local zoning laws and homeowner association rules.
- Interconnection Agreements: For grid-tied systems, establish interconnection agreements with your utility company.
17. Education and Awareness
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated with the latest advancements in solar technology and best practices.
- Community Engagement: Engage with local communities or online forums for support and shared experiences.

Detailed Steps for Installation
Step 1: Site Assessment
- Shading Analysis: Use tools like solar pathfinders to analyze shading throughout the year.
- Structural Assessment: Ensure the roof or ground structure can support the weight and wind load of the solar panels.
Step 2: Designing the System
- Electrical Design: Create detailed wiring diagrams showing panel connections, inverters, charge controllers, batteries, and disconnects.
- Component Sizing: Size each component based on the overall system capacity and expected energy output.
Step 3: Permitting and Approvals
- Submit Plans: Submit detailed plans and diagrams to local authorities for approval.
- Utility Coordination: Work with your utility provider for any required inspections and to set up net metering if applicable.
Step 4: Installation
- Mounting the Panels: Securely mount panels on the roof or ground mounts, ensuring proper tilt and orientation.
- Electrical Wiring: Run wiring from the panels to the inverters and other system components, following all safety guidelines.
- Connecting to the Grid: For grid-tied systems, connect to the utility grid following the approved interconnection procedures.
Step 5: Testing and Commissioning
- System Testing: Conduct thorough testing of the entire system to ensure it operates correctly.
- Performance Verification: Verify that the system meets expected performance metrics and energy output.
Step 6: Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular maintenance checks to ensure all components are functioning optimally.
- Troubleshooting: Develop a troubleshooting plan for common issues such as inverter faults, shading problems, or wiring issues.
Resources and Further Reading
- Online Courses and Certifications: Enroll in solar installation courses and certifications to deepen your understanding.
- Manufacturer Manuals: Refer to manufacturer manuals for specific installation and maintenance guidelines.
- Government Resources: Utilize government resources and programs for additional support and information on solar installations.
By carefully considering these tips and considerations, you can ensure a successful and efficient home solar power installation that meets your energy needs while promoting sustainability.