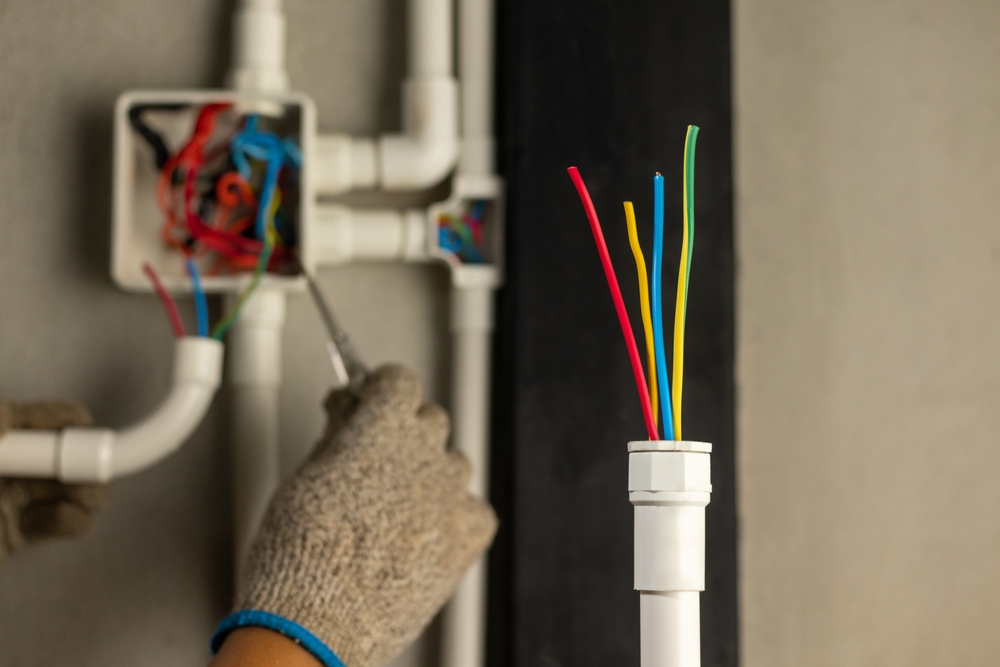
Ensuring the safety and efficiency of your home's electrical system is critical. Here are key points homeowners need to know about inspections and wiring:
1. Understanding Home Electrical Inspections
When to Get an Inspection
- Buying or Selling a Home: An inspection ensures the electrical system meets current safety standards.
- After Major Renovations: Any major electrical work should be inspected.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodic inspections (every 3-5 years) can prevent issues.
What Inspections Cover
- Wiring Condition: Checks for outdated, damaged, or improper wiring.
- Panel and Circuit Breakers: Ensures the panel is not overloaded and breakers function correctly.
- GFCI and AFCI Outlets: Verifies that Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI) and Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCI) are installed and working.
- Proper Grounding: Ensures the system is correctly grounded to prevent shocks.
- Overall System Load: Evaluates if the system can handle the home’s electrical load.
2. Basics of Home Wiring
Types of Wiring
- Knob-and-Tube: An older system, common in homes built before the 1950s. Not grounded and considered outdated.
- Aluminum Wiring: Used in the 1960s and 70s, can be a fire hazard if not properly maintained.
- Copper Wiring: The modern standard, known for reliability and safety.
Common Wiring Issues
- Outdated Wiring: Older systems may not meet current codes or handle modern electrical loads.
- Overloaded Circuits: Can cause breakers to trip or wires to overheat.
- DIY Fixes: Unqualified repairs can create hazards.

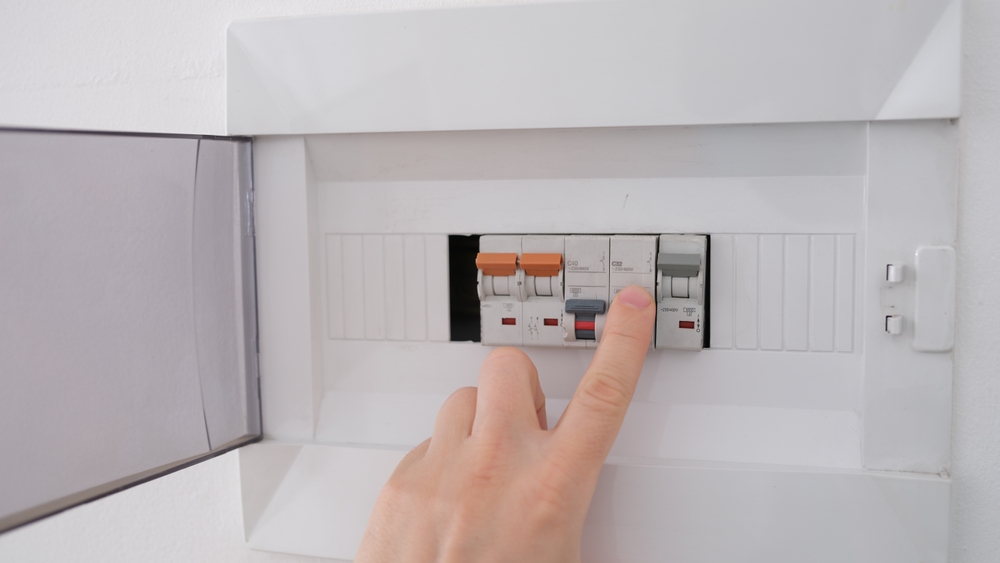
3. Safety Tips for Homeowners
Identifying Problems
- Flickering Lights: Can indicate loose wiring or circuit issues.
- Warm Outlets or Switches: May signal overloaded circuits or faulty wiring.
- Frequent Breaker Trips: Could mean overloaded circuits or short circuits.
Preventive Measures
- Avoid Overloading Outlets: Use power strips with surge protectors.
- Use Proper Extension Cords: Temporary use only, avoid overloading.
- Regular Professional Inspections: Essential for safety and compliance.
4. Upgrading Your Electrical System
Why Upgrade?
- Increased Safety: Modern systems are designed with safety in mind.
- Capacity Needs: Modern appliances and devices require more power.
- Home Value: An updated system can increase property value.
Common Upgrades
- Service Panel Upgrade: From 100 amps to 200 amps to handle more load.
- Installing GFCIs and AFCIs: For improved protection against shocks and fires.
- Whole-House Surge Protection: To protect appliances and electronics from power surges.
5. Working with Professionals
Hiring an Electrician
- Qualifications: Ensure they are licensed, insured, and have good reviews.
- Estimates: Get multiple quotes for large projects.
- Permits and Inspections: Ensure they handle necessary permits and inspections.
6. Electrical Code Compliance
Understanding Electrical Codes
- National Electrical Code (NEC): The NEC sets the standard for electrical safety in residential and commercial buildings in the United States. Familiarize yourself with basic requirements.
- Local Codes: Local jurisdictions may have additional or modified codes. Check with your local building department.
Importance of Compliance
- Safety: Codes are designed to minimize the risk of electrical fires and shocks.
- Legal Requirements: Non-compliance can result in fines and legal issues.
- Insurance: Many insurance companies require code compliance for coverage.
7. DIY Electrical Work
Know Your Limits
- Simple Tasks: Changing light fixtures, replacing outlets or switches can be DIY-friendly if you have basic knowledge and follow safety precautions.
- Complex Jobs: Upgrading panels, adding new circuits, or rewiring should be left to professionals.
Safety Tips for DIY Projects
- Turn Off Power: Always turn off power at the breaker before starting any electrical work.
- Use Proper Tools: Insulated tools and voltage testers are essential.
- Follow Instructions: Adhere to manufacturer instructions and local codes.
8. Energy Efficiency and Electrical Upgrades
Energy-Efficient Lighting
- LED Bulbs: Use less power and last longer than incandescent or CFL bulbs.
- Smart Lighting: Systems that can be controlled via apps can save energy and add convenience.
Smart Home Systems
- Programmable Thermostats: Help reduce energy consumption by optimizing heating and cooling.
- Energy Monitoring: Smart plugs and energy monitors can help track and reduce power usage.
Renewable Energy Integration
- Solar Panels: Installing solar panels can reduce dependency on grid electricity and lower utility bills.
- Battery Storage: Systems like Tesla Powerwall can store solar energy for use during outages or peak hours.
9. Dealing with Electrical Emergencies
Common Electrical Emergencies
- Electrical Fire: Use a fire extinguisher rated for electrical fires (Class C). Never use water.
- Power Outages: Have a generator or battery backup for critical devices.
- Electrical Shock: If someone is shocked, do not touch them directly. Turn off power and call emergency services.
Preparation Tips
- Emergency Kit: Keep a kit with flashlights, batteries, and first aid supplies.
- Know Your Breaker Panel: Label circuits and know how to turn off power quickly.
10. Maintaining Your Electrical System
Routine Checks
- Visual Inspections: Regularly check outlets, switches, and cords for signs of wear or damage.
- Test GFCIs and AFCIs: These should be tested monthly to ensure they’re functioning properly.
Professional Maintenance
- Annual Inspections: Have a professional check your system yearly, especially if you have an older home.
- Pest Control: Rodents can chew through wiring, so regular pest control can prevent damage.
11. Understanding Electrical Costs
Estimating Project Costs
- Material Costs: Wire, outlets, panels, and fixtures vary in price. Get a detailed list before starting a project.
- Labor Costs: Electricians typically charge hourly rates plus the cost of materials. Get multiple quotes.
- Permit Fees: Include the cost of permits in your budget.
Budgeting for Upgrades
- Prioritize Safety: Invest in critical upgrades like panel improvements and code compliance first.
- Plan for Future Needs: Consider your future electrical needs, like adding a home office or electric vehicle charger.
12. Electrical System Components
Service Entrance
- Main Service Panel: The central hub of your home’s electrical system, distributing power to various circuits.
- Meter: Measures electricity usage. Utility companies use this to calculate your bill.
- Service Disconnect: A switch that can shut off power to the entire house in an emergency.
Subpanels
- Purpose: Subpanels provide additional circuit capacity and are often used for additions or detached structures.
- Location: Typically located closer to the area they serve, reducing the need for long circuit runs.
Circuits and Breakers
- Standard Circuits: Handle general lighting and outlet loads.
- Dedicated Circuits: Required for high-demand appliances like refrigerators, microwaves, and HVAC systems.
- Circuit Breakers: Protect circuits by shutting off power if there’s an overload or short circuit.

13. Specialized Electrical Systems
Backup Generators
- Portable Generators: Useful for temporary power during outages. Ensure proper ventilation to avoid carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Standby Generators: Permanently installed, they automatically kick in during an outage and can power essential systems.
Home Automation Systems
- Lighting Control: Automate lighting to improve energy efficiency and security.
- Security Systems: Integrated systems can include alarms, cameras, and motion detectors.
- Smart Home Hubs: Control various devices through a single interface, such as Amazon Echo or Google Home.
14. Identifying Qualified Electricians
Credentials and Licensing
- Licensing: Ensure the electrician is licensed in your state or local jurisdiction.
- Certifications: Look for additional certifications, such as from the National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA) or International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW).
Experience and References
- Experience: Choose electricians with experience in residential projects similar to yours.
- References: Ask for and check references from previous clients.
Insurance and Warranties
- Insurance: Verify that the electrician has liability insurance and worker’s compensation.
- Warranties: A reputable electrician should offer warranties on their work and materials.
15. Common Electrical Projects and Their Considerations
Lighting Upgrades
- Recessed Lighting: Popular for a modern look and space-saving.
- Under-Cabinet Lighting: Adds functionality and aesthetics to kitchens.
Outlet and Switch Replacement
- Smart Outlets: Can be controlled remotely and monitored for energy usage.
- USB Outlets: Convenient for charging devices directly from the outlet.
Ceiling Fan Installation
- Benefits: Improves air circulation and can reduce HVAC costs.
- Considerations: Ensure the electrical box is rated for ceiling fan support.
16. Understanding Electrical Hazards
Fire Hazards
- Overloaded Circuits: Can cause overheating and fires.
- Old Wiring: Insulation degrades over time, increasing fire risk.
Shock Hazards
- Ungrounded Outlets: Can cause electrical shock if faults occur.
- Exposed Wiring: Damaged or exposed wiring poses a significant shock risk.
Preventive Measures
- Childproof Outlets: Use tamper-resistant outlets to protect children.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep wiring and components in good condition through regular inspections.
17. Sustainability and Electrical Systems
Energy Audits
- Professional Audits: Identify areas where you can improve energy efficiency.
- DIY Audits: Simple steps like checking for drafts and insulation can lead to savings.
Renewable Energy Solutions
- Solar Power: Reduces reliance on the grid and lowers energy bills.
- Wind Power: Another renewable option, though more location-dependent.
Energy-Efficient Appliances
- ENERGY STAR® Appliances: Use less energy and save money on utility bills.
- Smart Appliances: Can be programmed to run during off-peak hours to reduce energy costs.
18. Electric Vehicles and Home Charging
EV Chargers
- Level 1 Chargers: Use a standard 120-volt outlet, but charge slowly.
- Level 2 Chargers: Require a 240-volt outlet and charge much faster.
Installation Considerations
- Electrical Capacity: Ensure your home’s electrical system can handle the additional load.
- Permits and Inspections: May be required for installation of a Level 2 charger.